Despite the fact that today it is really possible to buy a ready-made structure, many people prefer to find out how to build a greenhouse with own hands.
A good quality greenhouse is the dream of any inveterate summer resident. It is a cheap, safe and certainly useful construction. Let’s look how to build a greenhouse and properly arrange it.
Choosing a place for greenhouses
 Everyone knows that plants cannot exist without sunlight. Therefore, to get a great harvest, it is necessary to arrange a greenhouse in such a way that through its coating will penetrate as much sunlight as possible.
Everyone knows that plants cannot exist without sunlight. Therefore, to get a great harvest, it is necessary to arrange a greenhouse in such a way that through its coating will penetrate as much sunlight as possible.
It is advisable to choose the area without trees and shrubs – this will avoid the creation of shadows. In addition, the greenhouse must be protected from drafts and wind. Therefore, it could be better to replace a construction near some buildings, such as near a summer kitchen and a shed.
Depending on the time when you are going to operate the greenhouse, there are two possible options for its placement. If it is only for the winter, you need to install a greenhouse from west to east. In this case you need to find out how to build a wooden greenhouse or glass greenhouse. If you are going to exploit it in spring and summer, so place it from the north to south. After contemplating these tips, choose the best location for your structure.
Let’ at the beginning understand what are general types of greenhouses, and then find out how to build your own greenhouse just in a single weekend.
Greenhouse types
The most common, comfortable and loved by summer residents are arched types, with one or two slopes greenhouses.
Arched greenhouses
An arched greenhouse has a roof in the shape of an arc, so plants receive more light because the sun rays are scattered by the arcuate surface, giving light and heat for carefully fostered greens. And on the arched roof snow in winter does not accumulate, thus your construction is not threatened the distortion or destruction (of course, if you have carefully strengthened its frame and foundation).
One slope greenhouses
One slope greenhouses are usually adjacent to a wall of a good solid cottage construction. Some gardeners park it in the southern part of the country house. This construction is very low cost and saves some extra space at the cottage plot. And if the building, to which a greenhouse adjoins, is well heated, then it is even better! You will spend less effort on its heating. But, unfortunately, the snow from the roof of a greenhouse does not roll down by itself and you have to watch it, regularly cleaning the greenhouse roof from snow drifts.
Two slopes greenhouses
 The most common type of greenhouses are constructions with two slopes, where the roof is framed by a triangle. The main advantage of this structure is a space for you and your plants. Some gardeners build even a greenhouse like a kind of recreation area, combining business with pleasure.
The most common type of greenhouses are constructions with two slopes, where the roof is framed by a triangle. The main advantage of this structure is a space for you and your plants. Some gardeners build even a greenhouse like a kind of recreation area, combining business with pleasure.
There are many design ideas for creating this construction. You may even decide on how to build a greenhouse from old windows. In addition, all types of greenhouses can be divided into winter and summer.
Winter greenhouses
Winter greenhouses must be necessarily heated, so think over it for a place closer to the communication system of the house, because the heating pipes you will connect to the centralized heating system. Although there is another option: a greenhouse equipped with a stove. But there is an extra trouble: the stove should be regularly flushing and constantly monitored by the temperature regime. When building a winter greenhouse with your own hands, it is necessary to put it on a solid foundation and strengthen well the base and roof. After all, under the weight of snow this structure can easily be deformed, if not destroyed, that also may happen.
Thermos greenhouse dug in the ground
It is possible to create a so-called thermos greenhouse, which is usually deepened into the ground at 40 inches. Accordingly, it is necessary to dig a trench under it, reinforce the foundation, erect the walls of the thermal blocks, make a special insulation, perform heating and other much more time-consuming and financially costly operations. Therefore, such a greenhouse is built much less other types of this construction.
Summer greenhouses
The summer greenhouse is usually called the one, which frame is covered with dense polyethylene film. This is the simplest and cheapest variant of cladding, and with careful use of plastic film it is fully capable to last for a couple of seasons. Under the film greenhouses, as a rule, builders should construct a wooden frame on which at spring the tight plastic film is snapped and attached to a wooden base by conventional nails with wide heads (you can fix it with the help of special building buttons). For a frame can be used plastic pipes of polyvinylchloride (PVC). It is not very difficult to understand how to build a pvc greenhouse even for cottagers, who do not have good skills in construction.
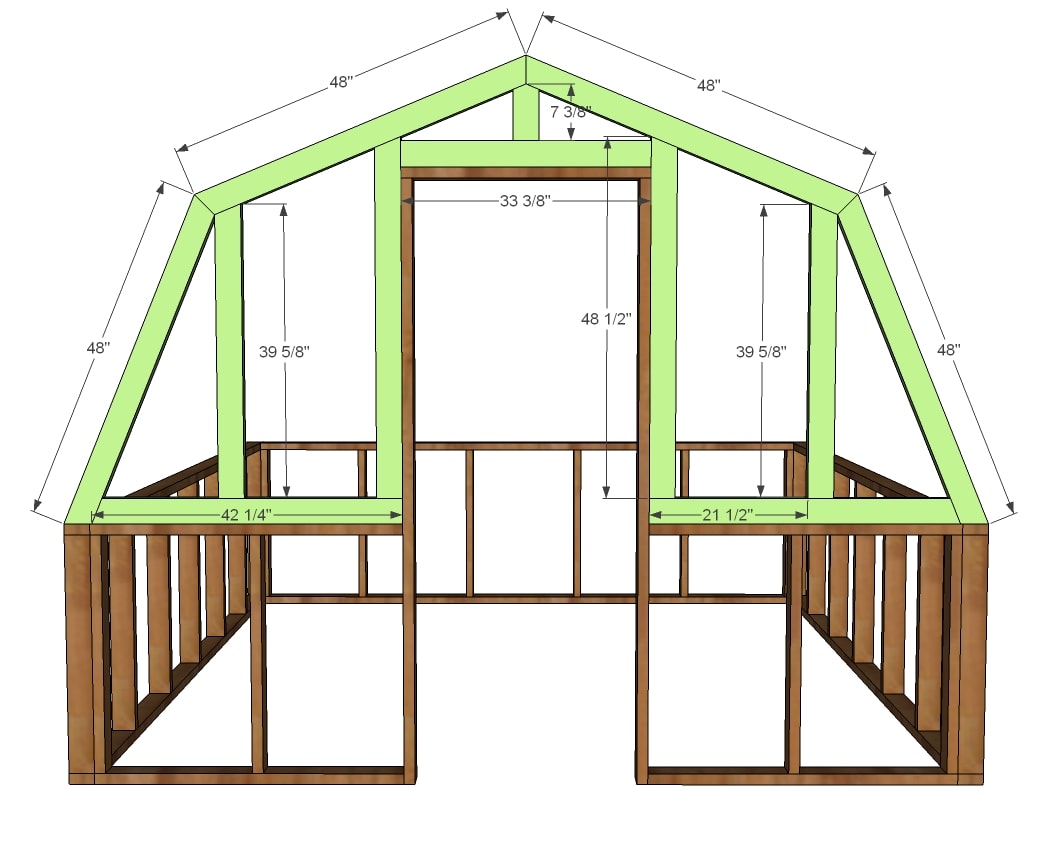
Construction process
The greenhouse consists of three main elements.
 The first one is the foundation. Construction of the foundation is the most time-consuming part of the whole work, but it influences on stability and reliability of the design. Once the location is selected, dig a trench around the whole perimeter of the greenhouse with installed depth of 16-20 inches. The bottom of the trench is filled with a sand layer (about 2 inches) as a cushion, then is rammed and poured with a gravel layer of 4 inches thick, laid with reinforcing mesh and poured with concrete.
The first one is the foundation. Construction of the foundation is the most time-consuming part of the whole work, but it influences on stability and reliability of the design. Once the location is selected, dig a trench around the whole perimeter of the greenhouse with installed depth of 16-20 inches. The bottom of the trench is filled with a sand layer (about 2 inches) as a cushion, then is rammed and poured with a gravel layer of 4 inches thick, laid with reinforcing mesh and poured with concrete.- Typically, the frame is made of wood or metal. Of course it is better to use galvanized steel pipe or galvanized profile. They do not rot, like wood, and do not rust during a long time.
- To make a roof, use a thick fishing line or nylon cord for a mesh frame, which in the future will not allow the roof to sag. On the frame top attach a film, nailing down to the construction bottom with the help of wooden bars.
When building the structure in the form of a house, all the edges have to be processed by special sealant. You spend more time on the rubbing edges and money sealant than get any benefit from such material savings. Polycarbonate sheets are fixed to the frame using screws.
When growing plants, you should also take care of the greenhouse heating and ventilation. Usually it is heated with electric heaters or stoves, solid fuel burning stoves.
Desirable to locate vents in the ceiling, as in that case the maximum ventilated space will be provided, while drafts are excluded.
Internal arrangement
The space inside of the greenhouse is necessary to be developed, taking into account the way in which it will be used. According to this principle greenhouses are divided into ground and shelving.
If a greenhouse is ground, then the first thing you need to plan the location of beds, namely to resolve the issue with their number, location and size. The width of single beds should not exceed 47 inches. This size will provide convenience in plants courting.
 As a rule, in small greenhouses two beds are equipped, running along the body. The path between them must have a width of not less than two feet. This is sufficient for the passage of a cart, which you should use when exporting of weeds and crops, besides it will allow to comfortable carry a bucket of water for irrigation, not touching the plants.
As a rule, in small greenhouses two beds are equipped, running along the body. The path between them must have a width of not less than two feet. This is sufficient for the passage of a cart, which you should use when exporting of weeds and crops, besides it will allow to comfortable carry a bucket of water for irrigation, not touching the plants.
The passage between the beds may be left as the ground, but when watering plants, puddles may be left there, which is not very convenient. The best option, which significantly saves costs for the construction of greenhouses, will be to lay out the passage with some old broken bricks. Such a coating in the wet condition will not slip and provide a clean operation.
The width of the rack construction should not exceed 37 inches for standing at the wall, and 59 inches for located in the middle. Again, the use of larger sizes will create inconvenience to the courtship of plants. Each homeowner has to choose the height himself, depending on his own height. It is great if this size will match the height of the kitchen table. The width of the passage in the greenhouse of the shelving type is similar to the size of the ground one.